- MP
- Blog
- Stakeholder Management
- Stakeholder Analysis & Mapping
Change management is an important process that requires careful planning, execution, and stakeholder engagement. Whether an organisation is implementing new policies or technology, or restructuring its workforce, understanding the key players involved is crucial to the project’s success. This is where stakeholder analysis and mapping play a pivotal role. Identifying, categorising, and strategically engaging stakeholders helps mitigate resistance, enhance buy-in, and drive a smoother transition.
Understanding Stakeholder Analysis in Change Management
Stakeholder analysis involves identifying individuals or groups affected by a change initiative and assessing their influence, interests, and potential impact. This analysis allows organisations to anticipate challenges and develop targeted strategies to address concerns.
Key aspects of stakeholder analysis include:
- Identification – Who are the stakeholders? Internal (employees, leadership) and external (customers, investors, regulators)
- Assessment – Understanding their influence, expectations, and concerns
- Engagement Strategy – How to communicate with and involve stakeholders effectively
The focus of this article will be on the analysis, assessment, and mapping of stakeholders once they have been identified. See our article on stakeholder registers here to find out more about the identification step.
The Role of Stakeholder Mapping
Stakeholder mapping is a visual representation of stakeholder relationships, influence, and engagement levels. By categorising stakeholders systematically, organisations can tailor their communication strategies and anticipate potential challenges. There are several different mechanisms for stakeholder mapping, we explore a few below.
Influence versus Interest Grid
One of the most effective tools for stakeholder mapping is the Influence versus Interest Grid, a 2 x 2 matrix that helps organisations determine:
- Who needs active engagement and buy-in,
- Which stakeholders’ power bases and interests must be considered, and
- Where alliances should be encouraged or managed carefully.
In this matrix, the x-axis represents stakeholder interest (how invested they are in the change initiative). the y-axis represents stakeholder influence (their ability to influence strategic outcomes).
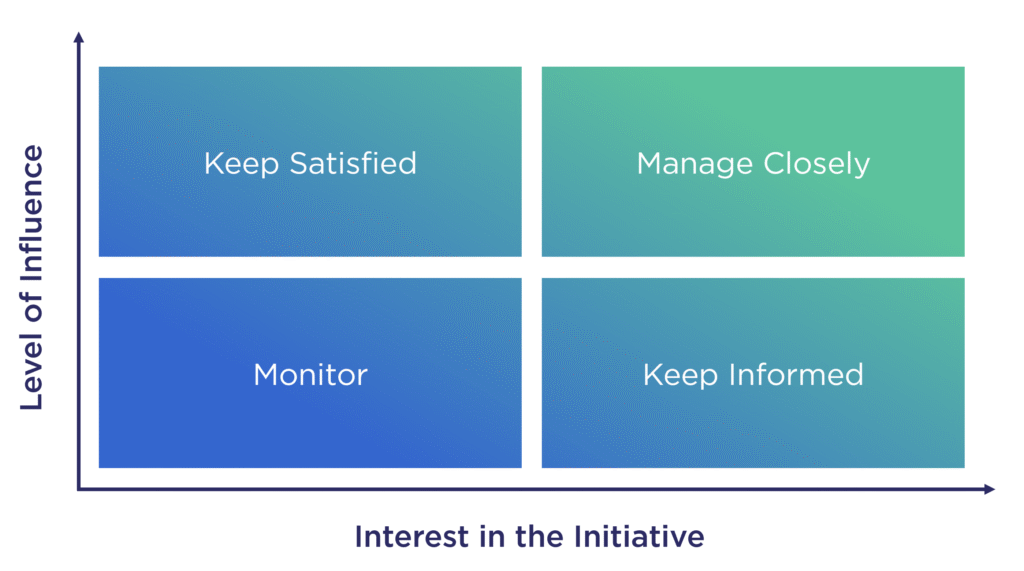
Stakeholders are mapped into four quadrants, which can help you to tailor your communications approach:
- High Influence – High Interest represents key decision-makers whose buy-in is crucial. Organisations must engage them proactively and ensure alignment.
- High Influence – Low Interest includes influential figures who are not highly engaged. Strategic communication can help maintain their support while preventing resistance.
- Low Influence – High Interest represents enthusiastic supporters who lack direct influence. Their energy can be leveraged to advocate for change and rally additional backing.
- Low Influence – Low Interest includes peripheral stakeholders with minimal involvement. While basic communication is required, extensive engagement may not be necessary.
Since stakeholder dynamics evolve, organisations must continuously track positioning on the grid to refine their engagement strategies. This helps identify coalitions, understand power shifts, and ensure stakeholders remain supportive throughout the change process.

Why Stakeholder Analysis and Mapping Matter
- Reducing Resistance to Change Resistance is a natural response to uncertainty. By understanding concerns and addressing them early, organisations can foster trust and minimise pushback.
- Enhancing Communication and Transparency Clear communication strategies, customised for different stakeholder groups, ensure alignment and reduce misinformation. Engaging stakeholders in decision-making also fosters inclusivity.
- Aligning Interests and Objectives Mapping stakeholder expectations against organisational goals helps create synergy and shared purpose, enhancing collaboration.
- Increasing Change Adoption and Sustainability A well-managed stakeholder engagement process accelerates acceptance, ensuring the change is not only implemented but sustained over time.
Benefits of Stakeholder Analysis and Mapping
Adopting a structured and proactive approach to stakeholder management offers substantial benefits. Among them is the ability to build strong, positive relationships with key stakeholder groups. These relationships foster early engagement and buy-in, which become invaluable when risks or issues arise. This allows teams to respond swiftly and collaboratively.
Beyond risk mitigation, consistent stakeholder engagement enhances overall project confidence. This is often driven by established communication channels, greater transparency, and a foundation of trust, all of which contribute to smoother decision making and stronger project outcomes.
Conclusion
Stakeholder analysis and mapping are fundamental components of successful change management. By identifying key stakeholders, assessing their influence, and strategically engaging them, organisations can navigate transitions more effectively, reduce resistance, and build a foundation for long-term success.


